Eagle’s eye
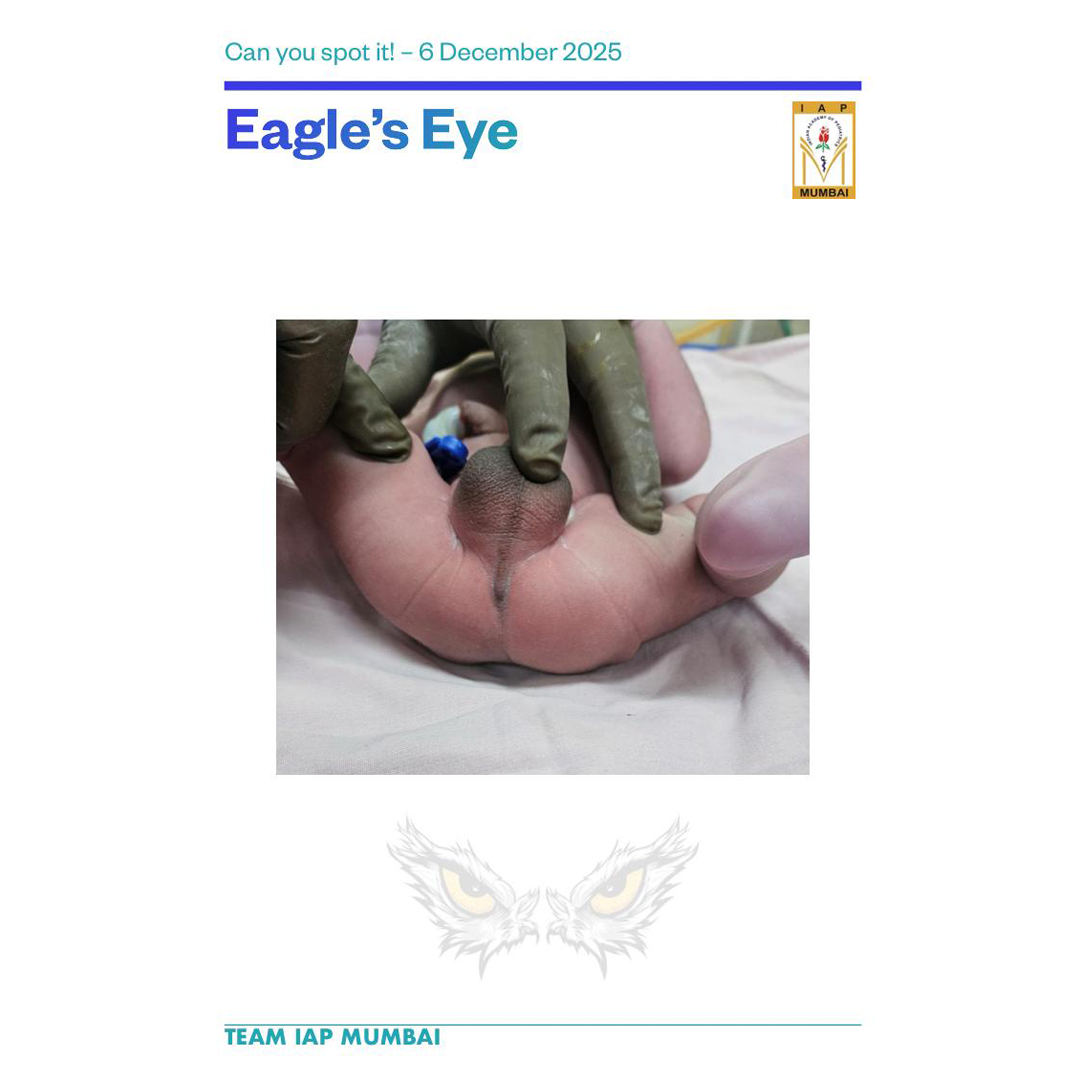
🌺Imperforate anus
It is a type of anorectal malformation where the normal anal opening is absent and may be part of a bigger anorectal malformation.
It is classified based on the position of the rectum relative to the sphincter complex:
Low lesions: Rectum has descended through the sphincter complex
High lesions: Rectum lies high above the sphincter mechanism.
Most babies have an associated fistula—in males commonly to the urethra or perineum, and in females to the perineum, vestibule, or as part of a cloaca.
Clinical clues:
Absent anal opening, meconium at abnormal sites, and abdominal distension if diagnosis is delayed.
Associated anomalies:
Frequently involves the genitourinary, vertebral, cardiac, gastrointestinal, and CNS systems. Always think of VACTERL.
Evaluation in the Newborn:
•The absence of an anal orifice in the correct position leads to further evaluation
•Inspect the perineum carefully for a fistula
•Prone cross-table lateral X-ray at 24 hours to determine the level
•Sacral X-ray for sacral anomalies
•Screen for esophageal atresia(NG tube test)
•Keep NPO, avoid rectal instrumentation
•USG abdomen, KUB, spine
•ECHO
•MCUG, vaginogram, and endoscopy may be required
Management:
Urgent pediatric surgical referral. Low lesions often undergo primary perineal repair; high lesions usually need a staged approach.
Long-term Issues:
Bowel continence, urinary function, and (in females) future reproductive outcomes.
🌺Team IAP Mumbai🌺
Additional Details
Show Hide Registration Button - Yes

